Computational Analysis of Communication
Mannheim Master in Data Science
Spring Term 2024
University of Mannheim
Welcome!
Welcome to this course!
- You can navigate through the sessions horizontally and within the sessions vertically
- Use your arrow keys
- Use
Mto open the menu - You can find the course website and all slides at https://felixdidi.github.io/24-1-ccs
- Press
?on your keyboard to learn more about how to navigate the slides!
Session 01: Introduction
Resources for this session
Episode 1 of CCS Podcast (Domahidi & Haim, 2021); Big Data, New Epistemologies and Paradigm Shifts (Kitchin, 2014)
Getting Started
What are the main questions to be answered in this session?
- What is this course about?
- What will I learn?
- What will I (have to) do?
Course Website
- Available at https://felixdidi.github.io/24-1-ccs
- Please read in detail after this session
Course material
- Will be provided via the course website (and ILIAS)
- Please sign up for the course on Portal2 (maybe?)
- You will be added to the ILIAS course automatically (maybe?)
- If you do not have access by the end of next week, please write an email
About

About Felix
- PhD-Student in Media Psychology
JGU Mainz - Teaching and Research Associate
JGU Mainz & Uni Mannheim
My research interests include:
- Digital autonomy and well-being
- Affordances of digital media & human-AI interaction
- Media entertainment experiences
- Open & computational communication science
What about you?
- Prior training (which Bachelor)?
- Experiences with communication science (or social science)?
- Experiences with R (or Python)?
- Prior knowledge on Webscraping, APIs, Survey Research, Inferential Statistics, Content Analysis / Text Mining?
Some Disclosures
Please be open to…
- …explore the social science part of CCS
- …learn R or Python if you have not done so yet
- …let me know if there is anything else you would like to cover in this course
Let’s solve some interesting problems together!
What Will I Learn?
Expertise
- Expertise in typical research topics and questions of CCS
- Knowledge of methodological approaches for tackling these questions (e.g., automated media content analysis)
- Knowledge about the methods’ potentials, limitations, and typical fields of application
- Ability to develop your own specific research questions
Methodological competence
- Independently develop a research question and design in the area of CCS
- Base assumptions on communication theory
- Conduct analyses using one of the methodological approaches introduced in the exercises
- Document the results of your analyses in a research report and reflect upon your findings’ limitations with regard to reliability and validity
Personal competence
- Developing problem-solving competences with regard to research-design oriented questions
- Transfer the learned material to related questions
- Independently tackling your own research-oriented tasks in the future
What Will I Do?
Live Sessions
- Attend the live sessions
Reading Task
- Read the provided literature to prepare for a live session
- Use the questions that are provided at the end of the previous session to guide your reading
- You should be able to provide answers to these questions in class
How to read, and how not to read?
- Don’t read scientific literature like a novel
- Start with Title, Abstract, Subheadings to get a first impression
- If your are reading digital, search for key words
- Think about “What do I want from this text?”
- Answer your own questions (I will also provide some)
What Will I Do?
Exercises (not graded)
- You will sometimes be provided with practical exercises
- These are intended to help you improve your competence with the learned methods
- Must be submitted after the live session via ILIAS
Graded Performance (“Prüfungsleistung”)
- To receive credit for this class, you must pass a “Prüfungsleistung”
- Two options: Individual or Group Research Report
Research Report
- Will be graded
- Must be submitted around end of semester (tbd)
- Typically in form of a rendered Quarto document (or, if you prefer that: as a jupyter notebook)
- No fixed length, but should deal with at least three hypotheses or research questions
Structure of Research Report
- Introduction: brief explanation of the topic & its relevance plus the methodological approach
- Literature review: (short) review of existing literature incl. derivation and formulation of hypotheses/research questions
- Method: description of the data set (origins & structure of the data, sampling approach, data preprocessing) and the analysis logic (incl. detailed explanation of used software packages & functions/models)
- Results: testing of hypotheses/answering of research questions (incl. data visualizations where applicable)
- Discussion: summary and interpretation of results, limitations of the methodological approach, outlook
Course Overview
Live Sessions
| Date | Topic |
|---|---|
| Apr. 12 | Introduction Opportunities, Challenges, and Pitfalls of Computational Communication Science How to Develop a Research Problem in Computational Communication Science? |
| May 3 | Project Weekend |
| May 4 | Project Weekend |
| May 5 | Project Weekend |
| May 17 | Project Presentation |
Any Questions?
Think about…
- What is a good definition of Computational Communication Science?
- Is the emergence of computational methods a paradigm shift for communication science? Why do you think so, why do you not think so?
Session 02: Opportunities, Challenges, and Pitfalls
 https://www.gocomics.com/calvinandhobbes/1990/06/09
https://www.gocomics.com/calvinandhobbes/1990/06/09
Resources for this session
When Communication Meets Computation: Opportunities, Challenges, and Pitfalls in Computational Communication Science (van Atteveldt & Peng, 2018)
Agenda
- Defining Computational Communication Science (CCS)
- Is CCS a Paradigm Shift?
- Theoretical Grounding of CCS
- Opportunities, Challenges, and Pitfalls
- The Computational Niche
What is CCS?

- Often, it is just a cool buzzword… 😎
- …that has no real basis and does not correspond to any common definition
Definitions of CCS
According to van Atteveldt & Peng (2018), CCS studies generally involve:
- large and complex data sets
- consisting of digital traces and other “naturally occurring” data
- requiring algorithmic solutions to analyze
- allowing the study of human communication by applying and testing communication theory
Three components according to Geise & Waldherr (2021):
- the analysis of social processes
- with (big) digital data on these processes
- the use of computer-based methods that allow a high degree of automation of the research process
So basically: New data & new methods, but same media & communication?
Taking a step back: What is communication?
The Lasswell Formula: “Who says what in which channel to whom with what effect?”
| Question | Element | Analysis | Example | CCS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Who? | Communicator | Control Analysis | Dory | ? |
| Says What? | Message | Content Analysis | “Just keep swimming!” | ? |
| In Which Channel? | Medium | Media Analysis | F2F (?) | ? |
| To Whom? | Audience | Audience Analysis | Marlin (?) | ? |
| With What Effect? | Effect | Effects Analysis | ? | ? |
Communication as the transmission of information…
…or the creation of meaning? (Berger & Luckmann, 1966)
A critical thought
“[Big data analytics] threatens to colonize the social sciences and humanities by turning these fields into computer science. If computational methods enter the curriculum of communication studies degrees in a major way that requires students to learn advanced programming, then not enough time will be left for practicing critical thinking, qualitative methods, social theory, critical theory, ethics, philosophy, history, and other crucial liberal arts skills because learning how to code properly is very time-intensive.”
— Fuchs & Qiu (2018)
So, what about theory?
What is “Theory”?
According to the APA Dictionary of Psychology…
- a principle or body of interrelated principles that purports to explain or predict a number of interrelated phenomena.
- in the philosophy of science, a set of logically related explanatory hypotheses that are consistent with a body of empirical facts and that may suggest more empirical relationships.
- in general usage, abstract or speculative thought as opposed to practice.
Is theory opposed to method then?
“There is nothing so practical as a good theory”
— Lewin (1951)
“There is nothing so theoretical as a good method”
— Greenwald (2012)
Analysis of two decades of Nobel awards in physics, chemistry, and medicine revealed that…
- existing theories were often essential in enabling development of awarded methods, and
- award-receiving methods often generated previously inconceivable data, which in turn inspired previously inconceivable theories
The end of theory?
The data deluge makes the scientific method obsolete (Anderson, 2008)
- by Chris Anderson (Editor in Chief of Wired)
- “Correlation supersedes causation” (e.g., shotgun gene sequencing of air)
- Models: Consistent, but imperfect
“We can stop looking for models. We can analyze the data without hypotheses about what it might show. We can throw the numbers into the biggest computing clusters the world has ever seen and let statistical algorithms find patterns where science cannot.”
— Anderson (2008)
- Seems to be a good method to maximize profits (e.g., Google, Amazon)
Four paradigms of science (Kitchin, 2014)
| Paradigm | Nature | Form | When |
|---|---|---|---|
| First | Experimental science | Empiricism; describing natural phenomena | pre-Renaissance |
| Second | Theoretical science | Modelling and generalization | pre-computers |
| Third | Computational science | Simulation of complex phenomena | pre-Big Data |
| Fourth | Exploratory science | Data-intensive; statistical exploration and data mining | Now |
Experimental science = pre-renaissance? 🧐
Is CCS a Paradigm Shift in Communication Science?
“Kuhn’s proposition was that a paradigm constitutes an accepted way of interrogating the world and synthetizing ideas and knowledge common to a substantial proportion of researchers in a discipline at any one moment in time”
— Kitchin (2014)

Thomas Kuhn (physicist & philosopher, “The structure of scientific revolutions”)
- Normal science
- Extraordinary research
- Adoption of a new paradigm
- Aftermath of the scientific revolution
Some Arguments
- Big Data can capture a whole domain and provide full resolution
- There is no need for a priori theory, models or hypotheses
- Through the application of agnostic data analytics the data can speak for themselves free of human bias or framing
- Meaning transcends context or domain-specific knowledge, thus can be interpreted by anyone who can decode a statistic or data visualization
- Big Data is both a representation and a sample
- Algorithms most certainly did arise and were tested scientifically for validity and veracity
- Making sense of data is always framed – data are examined through a particular lens that influences how they are interpreted
- Likely to be anaemic or unhelpful as it lacks embedding in wider debates and knowledge
Theoretical Grounding of CCS
“Because of their high level of abstraction, macro theories are often criticized for not being easily amenable to empirical research. For example, it is hard to directly derive testable hypotheses from abstract, overarching sociological concepts”
— Waldherr et al. (2021)
But, they can be helpful to answer questions such as:
- How do we make sense of the world?
- What is our research interest (explanation, description, norm-setting, or criticism)?
- Which actors and/or structures are important in explaining the social processes we want to study?
Answering these questions can be very helpful when evaluating or planning CCS research!
Opportunities, Challenges and Pitfalls of Computational Communication Science
- How can you leverage the opportunities of CCS with regard to your research interest?
- How can you avoid potential pitfalls with your research interest?
based on van Atteveldt & Peng (2018)
- From self report to real behavior
- From lab experiments to studies of the actual social environment
- From small-N to large-N
- From solitary to collaborative research
- How do we keep research datasets accessible?
- Is “big” data always good data?
- Are computational measurement methods valid and reliable?
- What is responsible and ethical conduct in computational communication research?
- (How do we get the needed skills and infrastructure?)
The Computational Niche
- How does you research interest fit the “computational niche”?
- How could you implement the recommendations proposed by Margolin (2019)?
Relationship between comparative advantages (rows) and recommendations (columns)
| Provide Multi-Causal Inventories | Report Informative Findings | Measure Important Variables “As Is” | Use Purposive Samples | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test External Validity | Fully articulate state of prior knowledge | Give “null finding” equal importance | Converts construct validity concerns to evaluations of theoretical boundary conditions | Guides field to deploy systematic, controlled variation across studies |
| Explore Theoretical Relevance | Identify when prior expectations are weak for relevant variables | Identifies theories that do and do not explain real world phenomena | ||
| Audition Hypotheses for Field | Provide all hypotheses that fit the data | Show that an effect holds in a specific, defined, sub-group and so may be generalizable | ||
| Create Unimaginable Hypotheses | Researchers must go beyond “most intuitive” explanation and acknowledge competing alternatives | Encourages theoretical interrogation of unexpected predictors | Reduce reliance on face valid comparisons that disguise counterintuitive differences |
Asking Meaningful Questions
based on Jungherr & Theocharis (2017)
- Using new data to reassess existing theories, but most importantly building new ones in light of new insights that could not have been acquired with previous research tools
- Developing new concepts and measures that, in combination, can help us better understand how attitudes and behaviors captured by this new data source map not only onto larger phenomena, but also onto our existing understandings, thereby making clearer what inferences we can—and cannot—draw in the study of complex social and political processes
- Reassessing our epistemological tools and methods and through interdisciplinary collaborations, reattuning them to synergize, rather than compete, with one another
- Making sure that this entire research program remains consistent with scientific values, ethics, and practices
Any Questions?
Session 03: Developing a Research Problem in Computational Communication Science
 https://www.gocomics.com/calvinandhobbes/1993/01/08
https://www.gocomics.com/calvinandhobbes/1993/01/08
Resources for this session
Forschungsmethoden und Evaluation in den Sozial- und Humanwissenschaften (Döring, 2022)
Agenda
- Developing a Research Problem
- Your Questions & Ideas
- Discussion
Developing a Research Problem
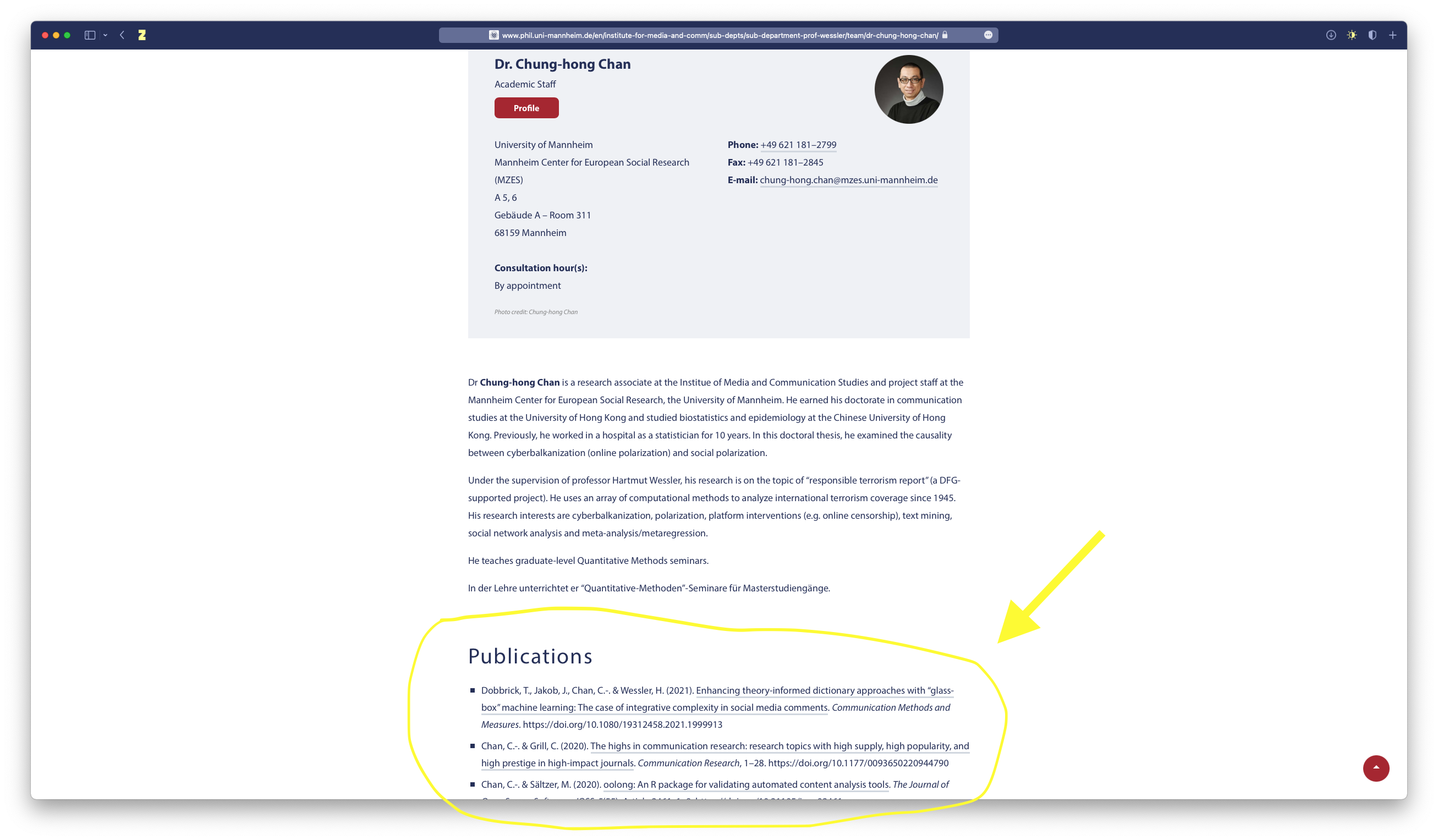
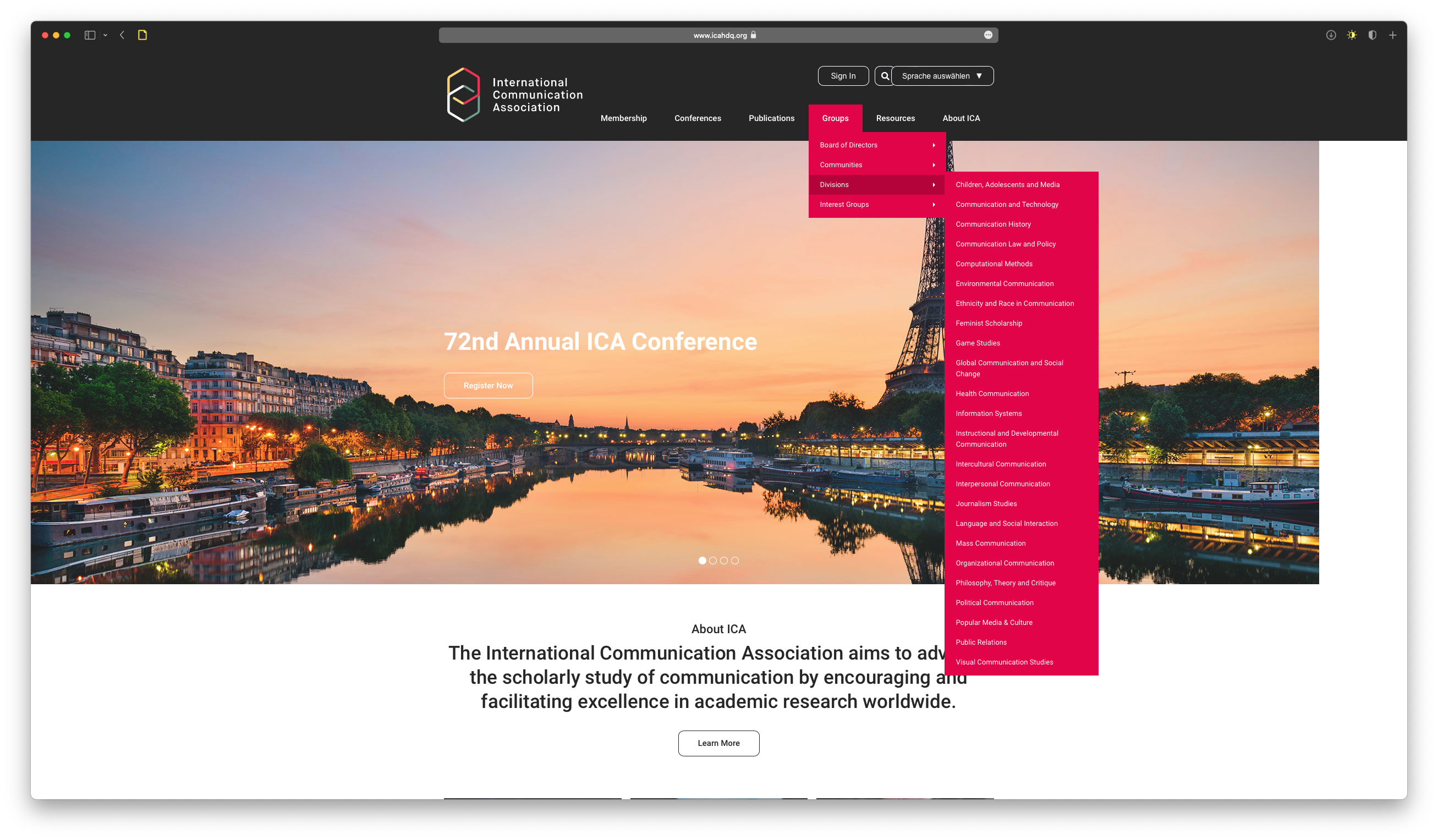
Get inspiration from publications of scholars who are active in the (C)CS community or from divisions and interest groups of the ICA.

Check out Communication Science Journals (maybe search for terms related to CCS)
- Communication Methods and Measures
- Computational Communication Research (rather new journal)
- Look for CCS special issues in other journals
Try to answer these questions:
- Who has an interest in the topic (e.g. scientists, practitioners, policymakers, particular members of society)?
- How much is already known about the problem?
- What is missing from current knowledge?
- What new insights will your research contribute?
- Why is this research worth doing?
Literature Research
- Google Scholar
- https://primo.bib.uni-mannheim.de/
- Communication and Mass Media Complete (CMMC)
- “Snowball” method and reverse citation search

Try to answer these questions:
- Compare and contrast: what are the main theories, methods, debates and controversies?
- Be critical: what are the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches?
- Show how your research fits in: how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize the work of others?
Any Questions?
Is social media bad for (adolescents) mental health?


What is (digital) psychological well-being?
“Optimal psychological functioning and experience”
Ryan & Deci (2001, p. 142)
- Focus on happiness and life satisfaction
- Pleasure attainment (positive affect)
- Pain avoidance (avoiding negative affect)
- Sometimes named subjective well-being
- Focus on full functioning
- Meaning
- Self-realization, self-actualization
Two-continua models of mental health
in the context of computer-mediated communication, see Meier & Reinecke (2021)
Possible Research Idea
Parasocial Phenomena
- The concept of parasocial interaction (PSI) goes back to Horton & Wohl (1956)
- In their research on the reception of TV presenters, they found that they often convey the illusion of direct interaction with the audience
- Television has no feedback channel, so parasocial interactions represent “illusory” relationships between media users and persona
- There is “perceived reciprocity” between media users and persona
- PSI arises through automated processes of social perception:
- We involuntarily categorize all objects in our environment into inanimate things vs. social actors
- Media personae are categorized and treated as social actors, although direct interaction with them is not possible
- see also Hartmann & Goldhoorn (2011), Rubin et al. (1985)
From PSI to PSR
- A number of influencing factors determine the strength of the PSI, e.g:
- The obtrusiveness of the persona, i.e. its media presence or intrusiveness
- The persistence of the persona, i.e. the duration and frequency of its appearance
- The direct address of the media user by the persona
- The attractiveness of the persona
- The degree of anthropomorphism (human likeness) of the persona and its closeness to reality (e.g. human vs. alien)
- Parasocial relationships can develop from PSI over time, which describe longer-term bonds with a persona
- Parasocial relationships do not usually represent intimate friendships and are no substitute for real relationships for the majority of recipients
- see, e.g., Tukachinsky & Stever (2019), Walter et al. (2023)
Former Student Project
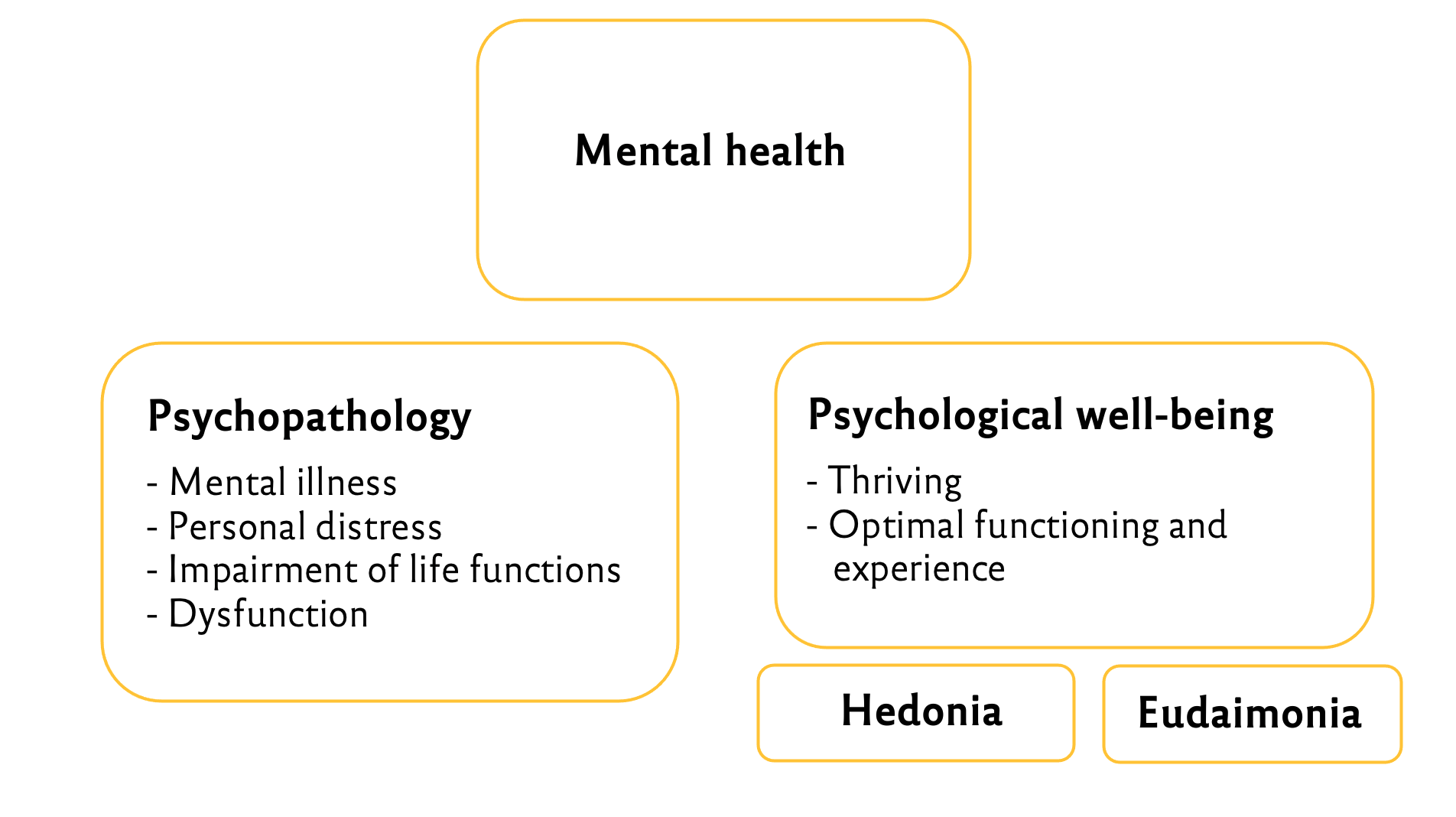
We assumed that…
H1: …the intimacy of a PSR increases over a) the duration of the relationship, as well as through more frequent information disclosure b) of the persona and c) of the recipient.
H2: …the intensity of a PSR increases over a) the duration of the relationship, as well as through more frequent information disclosure b) of the persona and c) of the recipient.
Discussion
Seminar Weekend: Day 1

Resources for this session
The Content Analysis Guidebook (Neuendorf, 2017)
Fundamentals of (manual) content analysis
Social Science Methods
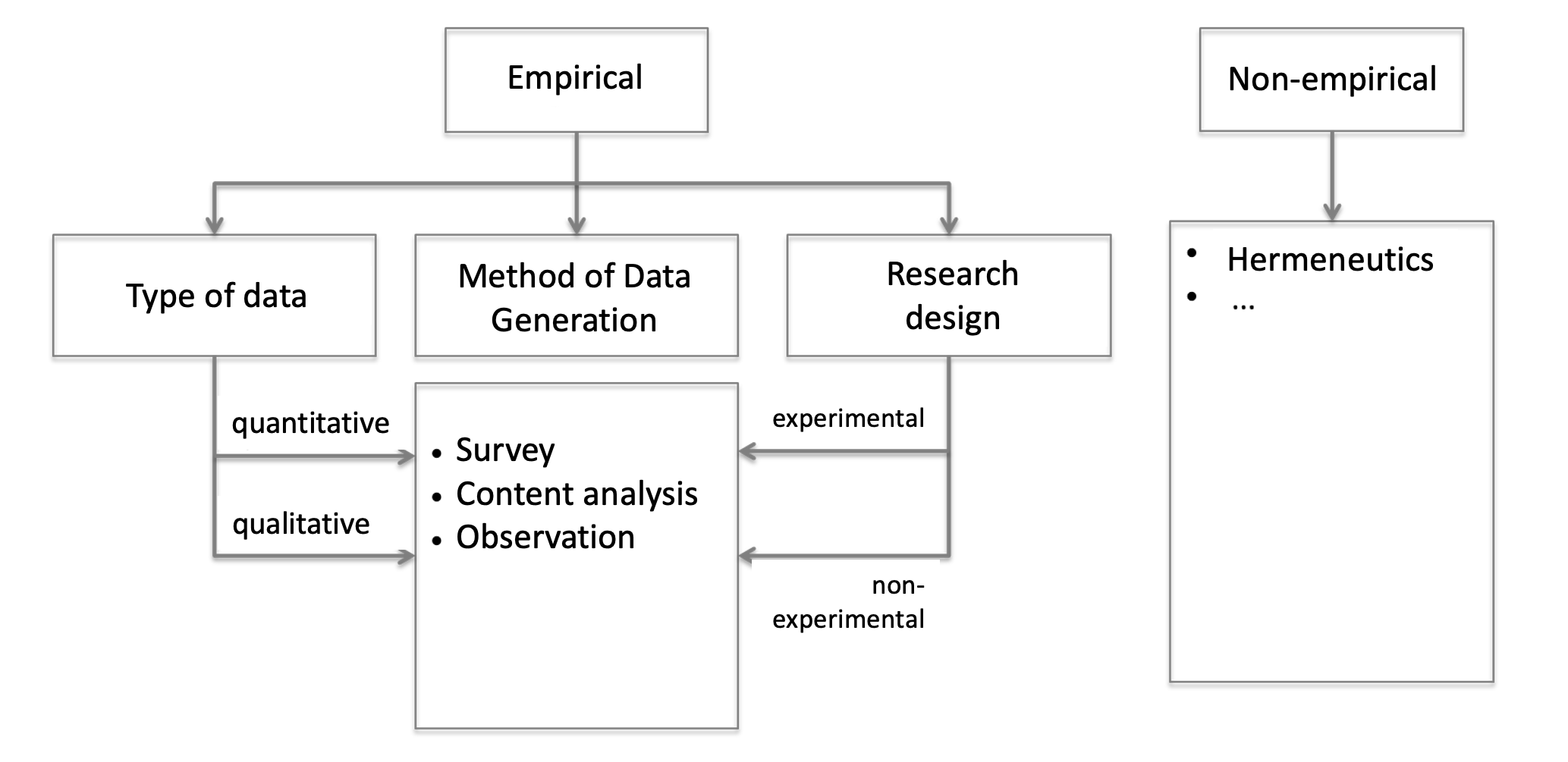
Defining content analysis
“Content analysis is a research technique for the objective, systematic, and quantitative description of the manifest content of communication.”
Berelson (1952, p. 18)
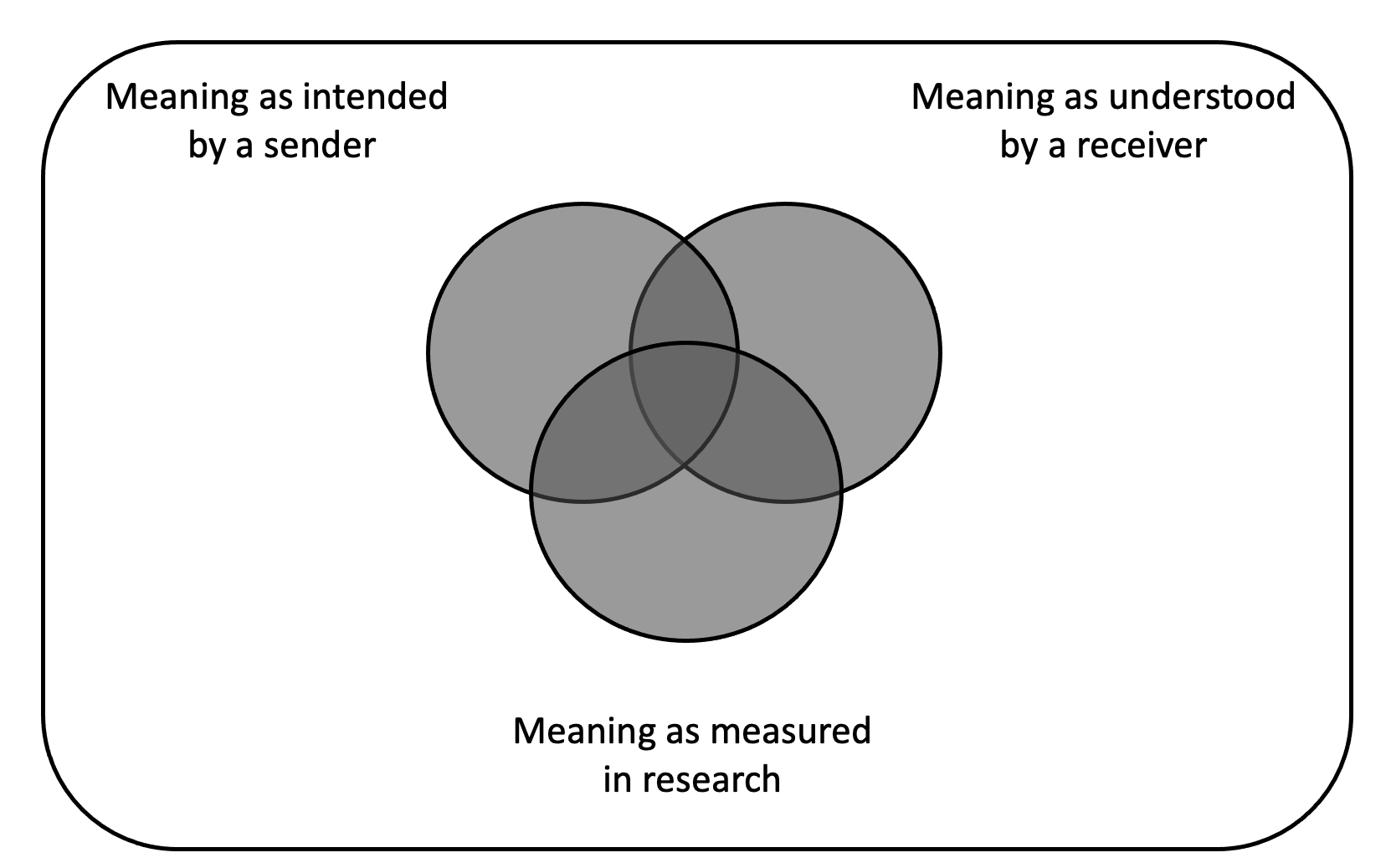
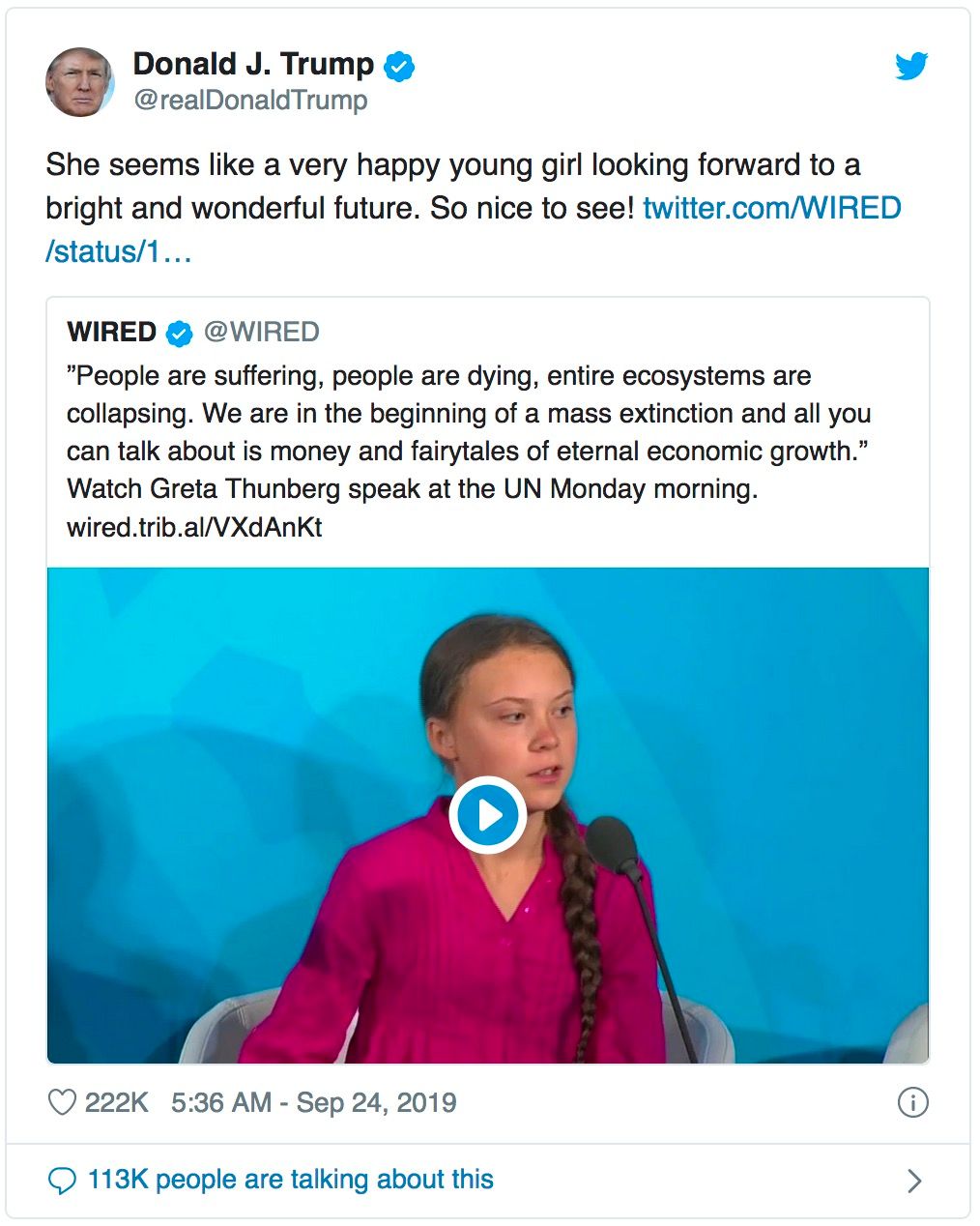
Is there a problem with this tweet?
Manifest vs. latent content
- Manifest: elements that are physically present and countable
- Latent: unobserved concept(s) that cannot be measured directly
- measured through coder assessment
- or multiple measures/indicators
“Content analysis is a research technique for making replicable and valid inferences from texts (or other meaningful matter) to the contexts of their use.”
Krippendorff (2018, p. 18)
“Content analysis is a summarizing, quantitative analysis of messages that follows the standards of the scientific method (including attention to objectivity–intersubjectivity, a priori design, reliability, validity, generalizability, replicability, and hypothesis testing based on theory) and is not limited as to the types of variables that may be measured or the context in which the messages are created or presented.”
Neuendorf (2017, p. 17)
The myths of content analysis
- Content analysis is limited to simple analyses
- Anyone can do content analysis; it doesn’t take any special preparation
- The term content analysis applies to all examination of messages (e.g., what about “qualitative content analysis”?)
- Content analysis is for academic use only
Can we only analyze whats “in” the text? (like the content of a container)
“The term ‘content’ in content analysis is something of a misnomer because verbal materials may be examined for content, for form (e.g., style, structure), function, or sequence of communications”
Smith (2000, p. 314)
Goals of content analysis
- Description of message content
- generally not problematic – but, see latent/manifest problem
- e.g., “To what extent do populist communication strategies appear in extremist propaganda videos?” (cf. Schmitt et al., 2018)
- Investigation of message quality
- requires a (normative) framework
- e.g., “Is there a difference between right-wing extremist and Islamist propaganda videos in terms of the use of populist communication strategies?” (cf. Schmitt et al., 2018)
- Inference
- requires additional data or profound theoretical assumptions
- prognostic inference (e.g., “What influence do populist communication strategies in extremist propaganda videos have on viewers?”)
- diagnostic inference (e.g., “Which elements of the discourse architecture promote the use of specific populist communication strategies?”)
Research objects
- Private communication, e.g., letters, private conversations, private messages
- Public communication, e.g., public speeches, media reportings of print, online, TV , & radio outlets, protocols of parliamentary debates, social media posts, ads, …
- Visual objects (photos, graphs, etc.) vs. written text vs. spoken text (has to be transcribed before analysis)
Potentials of content analysis
- Quantitative description of large amounts of messages
- Enables retrospective longitudinal designs
- No refusals or dropouts
- Non-reactivity
- Applicable to all forms of communication
Units
- Population: Full body of media messages that the study is supposed to draw conclusions about
- Units of investigation: Formally defined units (in codebook) that form the basis of an analysis, e.g. newspaper issues, Twitter posts from specific accounts within a certain time frime, etc.
- Units of analysis: Units to be coded and on which results shall be based (e.g. Tweets, articles, photos, paragraphs, sentences, words, etc.)
Which potential units of analysis do you see here?
Article level, paragraph level, sentence level, picture level, word level
Design decisions
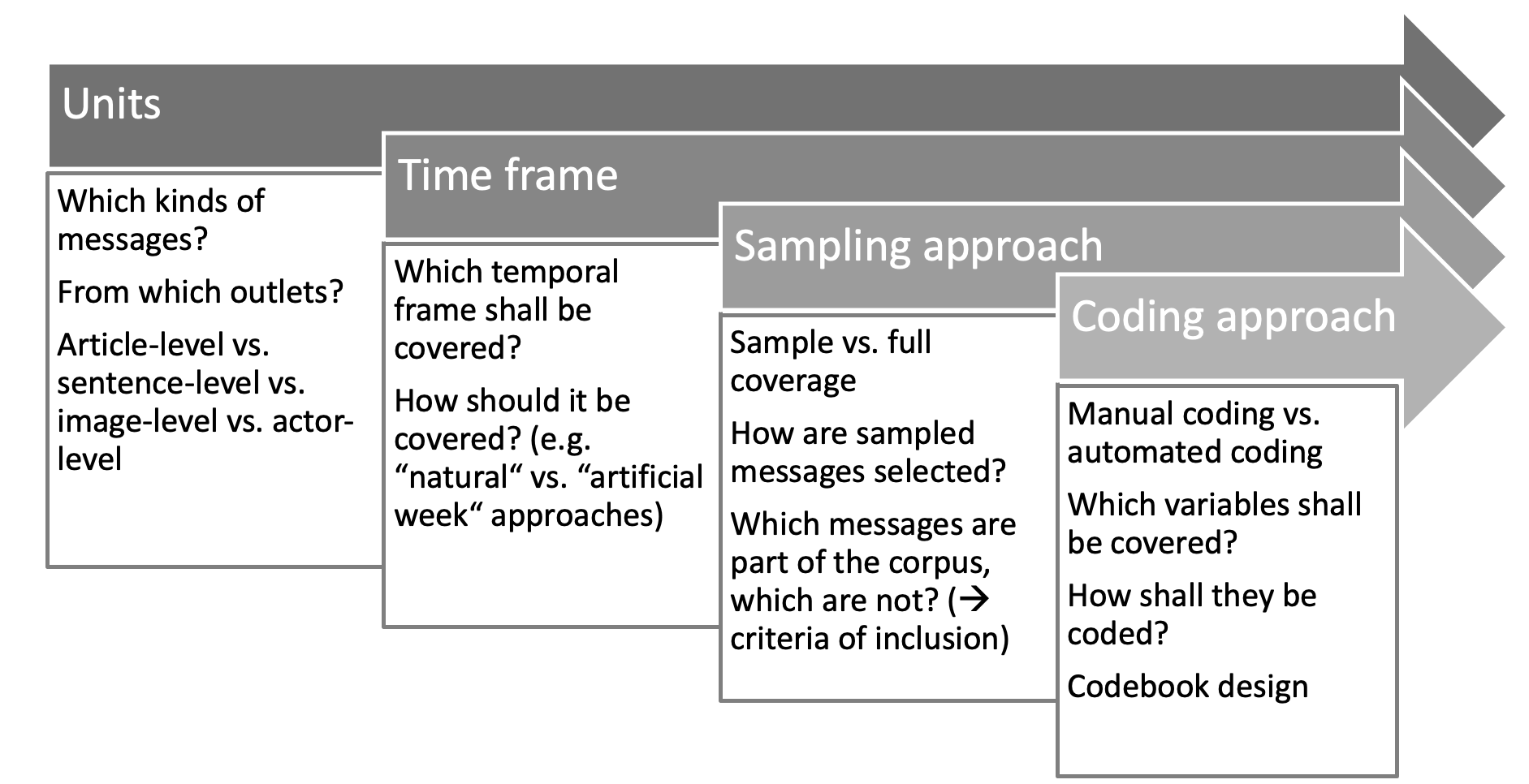
Materials for manual coding
- Codebook: System of rules and instructions for the selection and coding of messages
- Basic definitions of theoretical terms
- Units of investigation and analysis
- Criteria of inclusion
- System of categories to be coded
- Detailled coding instructions
- Coding scheme: Nowadays typically a data file in table format
- Coder training sessions and subsequent reliability testing
Example for a codebook here: https://osf.io/2z3dk/
Content Analysis as Following the Standards of the Scientific Method
“Content analysis is a summarizing, quantitative analysis of messages that follows the standards of the scientific method (including attention to objectivity–intersubjectivity, a priori design, reliability, validity, generalizability, replicability, and hypothesis testing based on theory) and is not limited as to the types of variables that may be measured or the context in which the messages are created or presented.”
Neuendorf (2017, p. 17)
Objectivity-Intersubjectivity
- Objectivity: Avoiding biases of the observer
- But: Social Construction of Reality

- Don’t ask: “Is it true?”, but “Do we agree it is true?”
- Intersubjectivity
A priori design
- Often violated in content analyses
- All decisions must be made before the final measurement process begins!
- variables
- their measurement
- coding rules
- Human coding: the codebook and coding form must be constructed in advance
- Automated coding: the dictionary or other coding protocol should be established a priori
In addition…
- Generalizability: see discussions about “The Computational Niche”
- Replicability: will be discussed
- Hypothesis testing based on theory: see discussions about “Theoretical Grounding”
- Reliability & Validity: Will be covered next
Validity
- Measurement Validity
- Measurement: the assignment of numerals to objects or events according to rules
\(measured score = true score + error score\)
- Potential causes of error
- coder misinterpretations
- coder inattention
- coder fatigue
- recording errors
- Random error
- generally summing to zero
- threat to reliability
- Nonrandom error
- bias
- threat to accuracy
Comparing Reliability, Accuracy and Precision
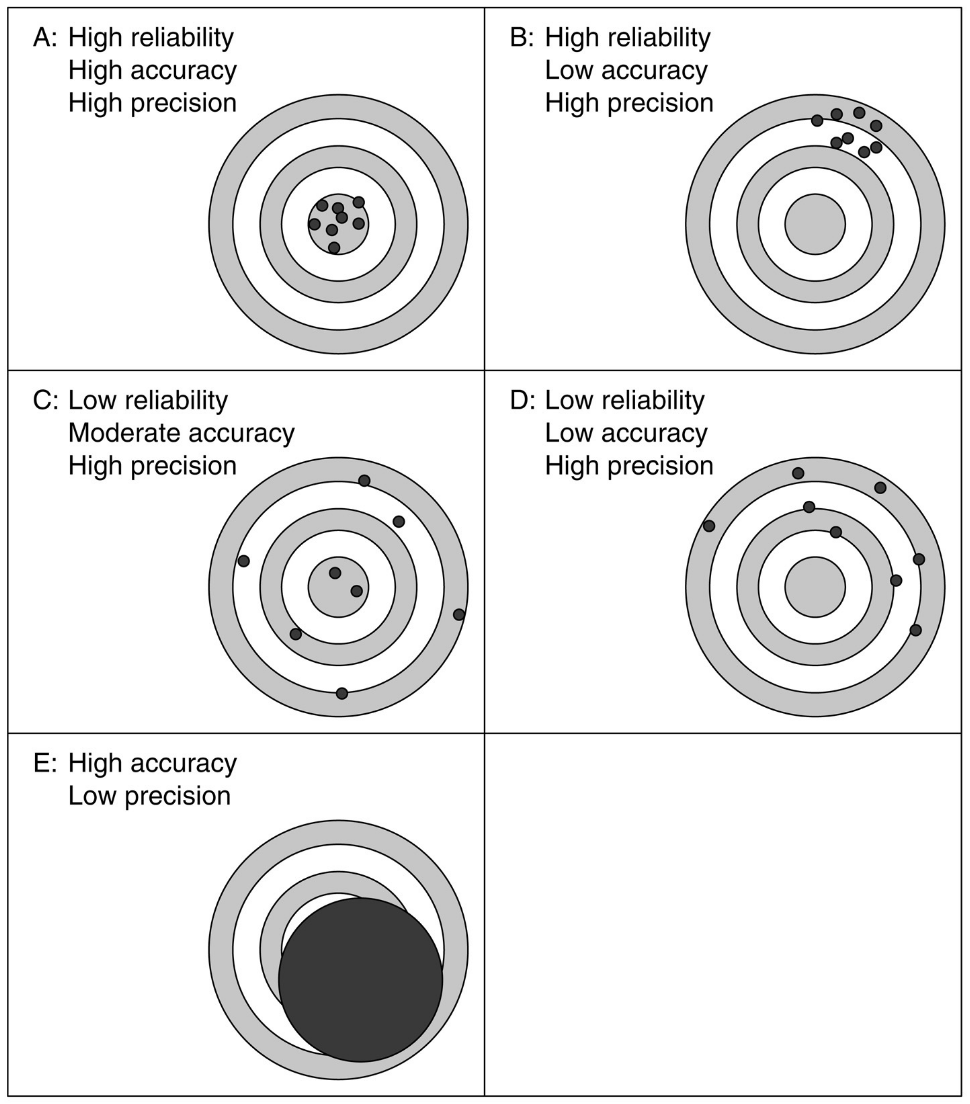
Types of Validity Assessment
- Internal Validity: matchup of a conceptual definition and an operational definition
- External Validity: can the results of a measure be extrapolated to other settings, times, and so on?
- representativeness of the sample
- ecological validity
- Face validity: the extent to which a measure—“on the face of things”—seems to tap the desired concept
- have others examine the measures without theoretical introduction
Types of Validity Assessment
- Criterion validity: the extent to which a measure taps an established standard or important behavior that is external to the measure
- concurrent: the standard or behavior exists at the same time as the measure
- predictive: the standard or behavior occurs after the measure
- Construct validity: the extent to which a measure is related to other measures (constructs) in a way consistent with hypotheses derived from theory
- convergent: an expected relationship is found between the measure and a validating measure
- discriminant: an expectation of no relationship between the measure and a validating measure is confirmed
- Content validity: the extent to which the measure reflects the full domain of the concept being measured
- goal: covering all important parts of the construct
Reliability
- The extent to which a measuring procedure yields the same results on repeated trials
- Intercoder reliability: the amount of agreement or correspondence on a measured variable among two or more coders or raters
- Intracoder reliability: the stability of a given coder’s measurements over time
- (Intercoder) Unitizing reliability: can coders agree on the delineation of units of data collection when that is part of the coding protocol?
Krippendorffs Alpha (Krippendorff, 2004)
Measure of intercoder reliability
\(alpha = 1 - \frac{D_{O}}{D_{E}}\)
\(D_{O}\) = observed disagreement
\(D_{E}\) = expected disagreement
For discussion of different reliability indeces, cf. Neuendorf (2017)
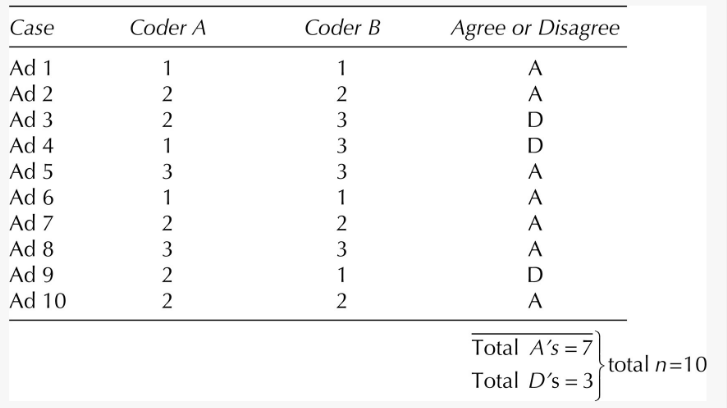
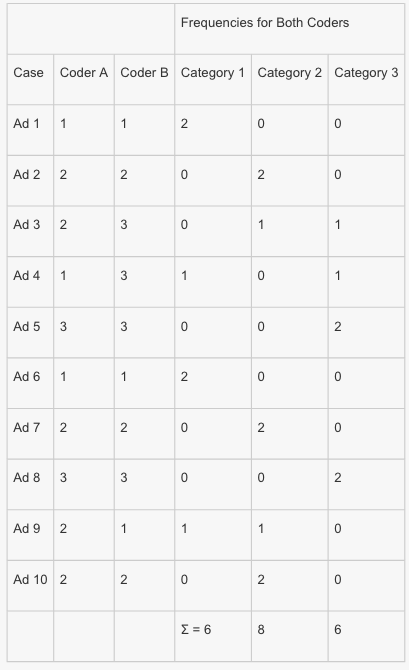
An example
\(alpha = 1 - \frac{nm - 1}{m-1} (\frac{\sum pfu}{\sum pmt})\)
\(pfu\) = product of any frequencies for a given case that are different (i.e., show disagreement)
\(pmt\) = each product of total marginals
\(n\) = number of cases coded in common by coders
\(m\) = number of coders

- pfu = (1 × 1) + (1 × 1) + (1 × 1) [disagreements for Cases 3, 4, and 9] = 3
- pmt = (6 × 8) + (6 × 6) + (8 × 6) [all pairings are added] = 132
\(alpha = 1 - \frac{(10)(2) - 1}{2-1} (\frac{3}{132})\)
\(= 1 - \frac{19}{1}(\frac{3}{132})\)
\(= 1 - 19(.023)\)
\(= 1- .43\)
\(= .57\)
Interpretation of Krippendorff’s Alpha: ≥ .667 (acceptable); ≥ .8 (good)
Reliability Analysis in R
References